Kawi
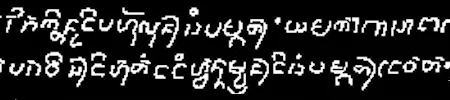
Script details
Section titled “Script details”See all script details: code, region, status and more
| Code | Kawi |
| Script type | abugida |
| Region | Mainland Southeast Asian |
| Status | Historical |
| Direction | LTR |
| Baseline | unspecified |
| Case | no |
| White space | none |
| Complex behaviors | |
| OpenType code | kawi |
| ISO 15924 Number | 368 (alphasyllabic) |
Script description
Section titled “Script description”The Kawi script descended from the Grantha script around the 8th century BC and was used across the islands of Borneo, Java, Bali, and Sumatra.
Read the full description…
The script originated in Java, and as a result is also sometimes called Old Javanese.
Kawi was an abugida; consonant characters are read with an inherent vowel. Diacritics are added to the consonant either to suppress the vowel entirely or to change it to a different vowel.
The Kawi alphabet developed around the 16th century AD into the current Javanese script. This transition was more stylistic than structural; the visual composition of the script changed but the way it worked stayed the same.
Languages that use this script
Section titled “Languages that use this script”| Language | Writing System Code | Writing System Status | SLDR/CLDR locale | Regional variants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kawi | kaw-Kawi | in use | kaw-Kawi-ID | |
| Old Malay | omy-Kawi | in use | omy-Kawi-MY | |
| Old Sundanese | osn-Kawi | obsolete | osn-Kawi-XX | |
| Sanskrit | sa-Kawi | in use | sa-Kawi-IN (India) |
Unicode status
Section titled “Unicode status”In The Unicode Standard, Kawi script implementation is discussed in Chapter 17 Southeast Asia-II — Indonesia and the Philippines and in UTN 48: Implementing Kawi.
Resources
Section titled “Resources”- ScriptSource page for Kawi script - all about scripts, languages, and writing systems